On this page
Introduction to Optimum Design
4. Optimum Design Concepts: Optimality Conditions
- 이 장의 주요내용:
비제약조건 및 제약조건 최적화 문제에서 국소적 및 전역적 최소(최대) 정의
비제약조건 최적화 문제에 대한 최적성 조건의 기술
제약조건 최적화 문제에 대한 최적성 조건의 기술
비제약조건 및 제약조건 문제에서 주어진 점에 대한 최적성 조건의 검토
후보 최소점을 위한 1차 최적성 조건의 풀이
함수와 설계 최적화 문제의 볼록성 검토
제약조건의 변동에 따른 목적함수의 최적값 변화를 연구하기 위한 라그랑지 승수의 활용
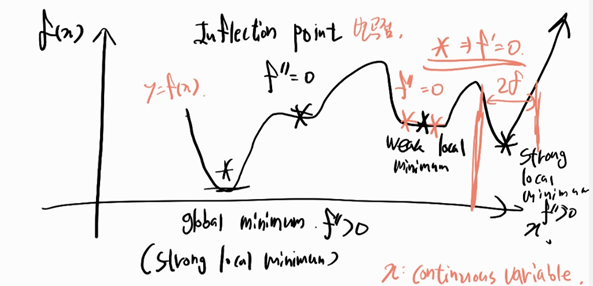
4.1 Global and local minima
minimum ← sigular, minima ← plurar
Global minimum
\(f(x^*) \le f(x)\quad \text{for all}\ x\ \text{in the feasible set, }S\)
Local minimum
\(f(x^*) \le f(x)\quad \text{for all}\ x\ \text{in a small neighborhood}\ N\ \text{of}\ x^* \text{in the feasible set, }S\)
\(N = \{x|x\in S\ \text{with}\ ||x-x^*|| < \delta\}\) where \(\delta\): small real number.
Existence of a minimum
Weierstrass theorem(필요조건, 만족안해도 미니멈 존재할 수 있음)
\(f(x)\) is continuous on a non-empty feasible set S that is closed and bounded, then \(f(x)\) has a global minimum is S.
set S is closed \(\Leftrightarrow a\le x \le b\)
set S is bounded \(\Leftrightarrow\) any \(x\in S, x^Tx<c\)
- c는 상수, \(x\)는 single이면 \(x^2<c\)
e.g.,
[0,1] : closed, bounded.
[2n, 2n+1], \(n \in Z\)(정수) : closed, but not bounded (\(\because n\rightarrow \infty\))
(0, 1] : not closed, but bounded
(2n, 2n+1) : not closed, not bounded
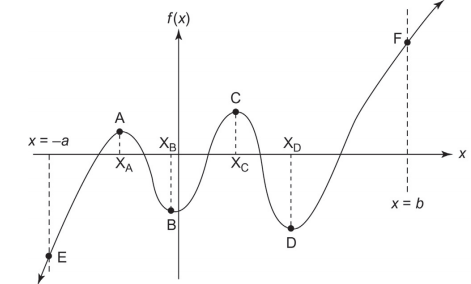
\(a\le x \le b\) : closed.
Any \(x \in S, \quad x^Tx < c\) : bounded
→ global minimum exist
4.2 Basic calculus concepts
Vectors
Sets
4.2.1 Gradient vectors (first-order partial derivative of a function)
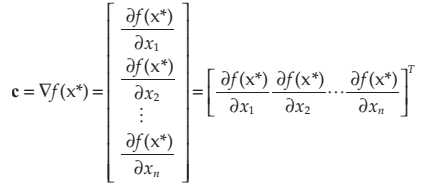
4.2.2 Hessian matrix (second-order partial derivatives)
\(\nabla^2f = \mathbf{H}\)
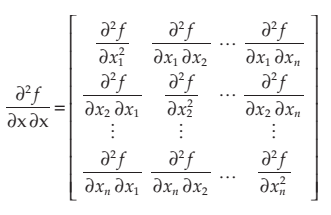
\(\mathbf{H} = \mathbf{H}^T\) (always symmetric)
4.2.3 Taylor’s Expansion
single variable \(x\)
\[f(x)=f(x^*) + \frac{df(x^*)}{dx}(x-x^*) + \frac{1}{2}\frac{d^2f(x^*)}{dx^2}(x-x^*)^2+ \cdots\]
Let \(x-x^* = d\)
\[f(x^*+d) = f(x^*) + \frac{df(x^*)}{dx} d + \frac{1}{2}\frac{d^2f(x^*)}{dx^2}d^2 + \cdots\]
Two variables, \(x_1\) and \(x_2\)
\[f(x_1^* + d_1, x_2^*+d_2) = f(x_1^*, x_2^*) + \frac{df}{dx_1}d_1 + \frac{df}{dx_2}d_2 + \frac{1}{2}\{\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x_1^2}d^2 + 2\frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x_1 \partial x_2}d_1 d_2 + \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x_2^2} d_2^2 \} + \cdots\]
Using summation notations,
\[= f(x_1^*, x_2^*) + \sum^2_{i=1} \frac{\partial f}{\partial x_i} d_i + \frac{1}{2}\sum^2_{i=1}\sum^2_{i=1} \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x_i \partial x_j} d_i d_j + \cdots\]
Using matrix notation,
\[f(\bar{x}^* + \bar{d}) = f(\bar{x}^*) + (\bar{\nabla}f)^T\bar{d} + \frac{1}{2} \bar{d}^T \bar{H} \bar{d} + \cdots\]
Let \(\Delta f = f(\bar{x^*} + \bar{d}) - f(\bar{x^*})\)
\[\Delta f = (\bar{\nabla}f)^T \bar{d} + \frac{1}{2} \bar{d}^T \bar{H} \bar{d} + \cdots\]
- \(\bar{x}, \tilde{x} \rightarrow\) 벡터나 매트릭스. multiple variable notation.
4.2.4 Quadratic form (Q-form) and definite matrix
Q-form
\[f = \sum^n_{i=1} \sum^n_{j=1} p_{xj} x_i x_j = \bar{x}^T \bar{P} \bar{x} \leftarrow \text{(Q-form)}\]
e.g., \(f = x_1^2 - 6x_1 x_2 + 9 x_2^2\)
\(= (x_1\ x_2) \begin{bmatrix} 1 & -3\\ -3 & 9 \end{bmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} x_1\\ x_2 \end{pmatrix} = \bar{x}^T \bar{P} \bar{x}\)
Positive definiteness (P-D) of Q-form
P-D if \(f(x)>0\) for all non-zero \(\tilde{x}\)
- 아래로 볼록! convex
P-semi D if \(f(\tilde{x}) \ge 0\) for all \(\tilde{x}\)
e.g., \(f=\frac{1}{3} x^2\) : P-D
\(\quad \quad f>0\) for \(x\neq0\)
\(\quad \quad f=0\) iff \(x=0\)
- negative는 위로 볼록, minimum 없음.
How to check P-D of \(\tilde{x}^T \tilde{P} \tilde{x}\)
check eigenvalues of \(\tilde{P}\)
sylvester’s test